Have you ever wondered why your candle flames will not have a shadow cast on a wall if you shine a torch on it? You can only see the outline of the candle, but the flame is invisible.
A source of light cannot produce a shadow. Flames are gaseous, and a light beam will easily sail through them. A shadow will only occur if an obstacle such as a carbon soot build-up will obscure the path of the light beam.
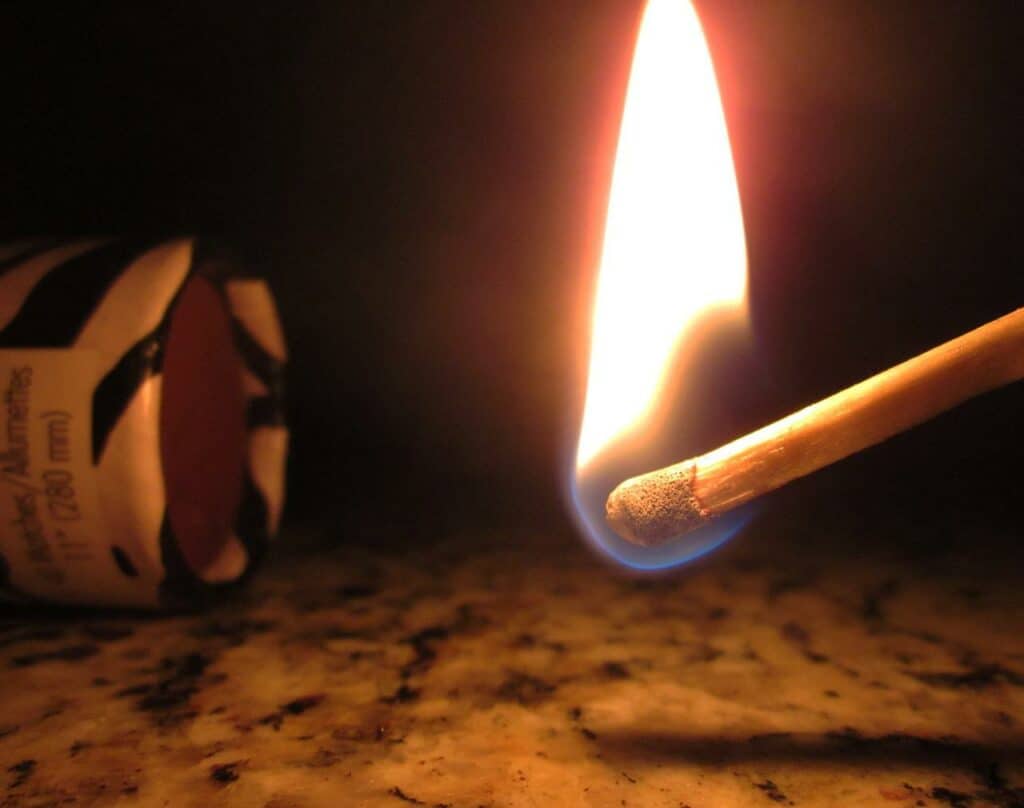

Do Flames Have Shadows?
Light and heat are the by-products of the rapid chemical combustion process. As the fuel source and oxygen react, we can feel the heat and see the light emission in the form of flames.
The flame is not usually straight and seems to be dancing or wiggling. This phenomenon occurs due to the flame being hotter than the surrounding air.
As the air warms up around the flame, it rises, and cool air fills the void. There is a steady cycle of conventional air currents.
Shadows occur both when there is light and darkness, depending on the positioning of the light source. When you shine another light source onto the flame, it neutralizes it, and you end up with no shadow.
Why Don’t Flames Have a Shadow?
To understand flames, first and foremost, we should understand how a shadow occurs. Typically, light travels in a straight line. A shadow occurs when an opaque object obstructs or scatters the light beam. The effect is a dark area or shape around the object where the light rays are the dimmest.
A flame is a light source, and another beam of light passing through it can’t cast a shadow. The light rays cannot interact directly because of photons, the basic unit of all light forms.
Photons are gauge bosons. Bosons control the interaction of the fundamental physical forces. These particles will allow other protons to overlap, pass through and occupy the same quantum state. It explains why light beams cannot absorb or bounce off each other.
Besides, photons have no electric or magnetic charge. Consequently, with one light beam unable to bond with another, each beam independently determines its beam path and activity.
Another reason why flames don’t have shadows is they have very low densities compared to the surrounding air. Gases, the primary components of all flames, are transparent except for a few impurities. When you focus a light beam on a flame, most of it will be able to sail without any refraction.
Here are a few experiments to try at home to find out if flames produce shadows:
Is Flame Matter or Energy?
By definition, matter is anything that has mass and occupies space. A flame is the light produced when a combustible material and a mixture of gases burn rapidly at high temperatures.
Consequently, a flame is an energy since it’s not necessarily a substance but a change in energy state. They have zero mass and depending on the frequency; they can carry energy and momentum.
Why Do Flames Have Different Colors
The colors of a flame are usually indicative of the degree of combustion or the flame temperature. Depending on the oxidation rate, different flame parts will have multiple colors.
The hottest part of the flame is at the base and is synonymous with a blue flame. You can expect temperatures of over 2500°C depending on the fuel type, such as natural gas, wood, or oil. Since the flame is nearest to the fuel source, there is complete combustion.
White, yellow, orange and red flames are what you’ll see as you move towards the outer layers of the flame. These colors stem from the incandescence of the soot particles as a result of incomplete combustion. The red color denotes a high number of pollutants and has the lowest temperature.
Does Water Have a Shadow?
Transparent objects DO NOT form shadows. When water is pure, there will be no shadows since there are obstructions on the light pathways. It will allow light to pass through completely.
A shadow is not a reflection, even though people use them interchangeably. The shapes might be similar to the object, but these two are distinct. A shadow means light cannot get through to the other side of the material, while reflection is the change in the direction of light rays.
Water bubbles, however, are not entirely transparent. Light rays will get refracted, and as a result, you will have shadows outlining the edges of the bubbles.
Can A Flame Cast A Shadow?
While a flame can cast a shadow, it does not correlate with light. The shadows result from the emission of pollutants such as soot/smoke during combustion. These solid impurities will deflect, block or absorb some of the light beams, causing the formation of a shadow.
For you to notice a shadow of a flame, the light beam going through it should be brighter. For instance, you can’t use a flashlight to see the flames of a campfire.
The flames of the fire will absorb the beam and neutralize any dim spots. The bigger the flame, the bigger and brighter the light beam ought to be.
Sometimes, shadows may be present but invisible to the naked eye. If the flame is small or undergoes high combustion, only the faintest edges of the flame will be visible.
Final Words
As illustrated in the article, not every medium that gets in the way of a light beam can cause a shadow. Other sources of light and transparent objects are good examples of items that will allow light to flow through them.
While flames don’t usually cast shadows, incandescence causes deflection of light beams making flames have shadows. It is purely because of some impurities and incomplete combustion of fuels. Under optimal conditions, this will not happen.